Solar Panel Mounting Brackets A Complete Guide (2025)
Your solar power system requires the proper support system of solar panel mounting brackets. The solar panels cannot maintain steady performance and stay safe without brackets. Being a homeowner, contractor, or business owner looking into solar, you need proper bracket selection to make your setup successful.
Our information explains essential features of solar panel brackets plus available setups while guiding you to select an ideal system.
What Are Solar Panel Mounting Brackets?

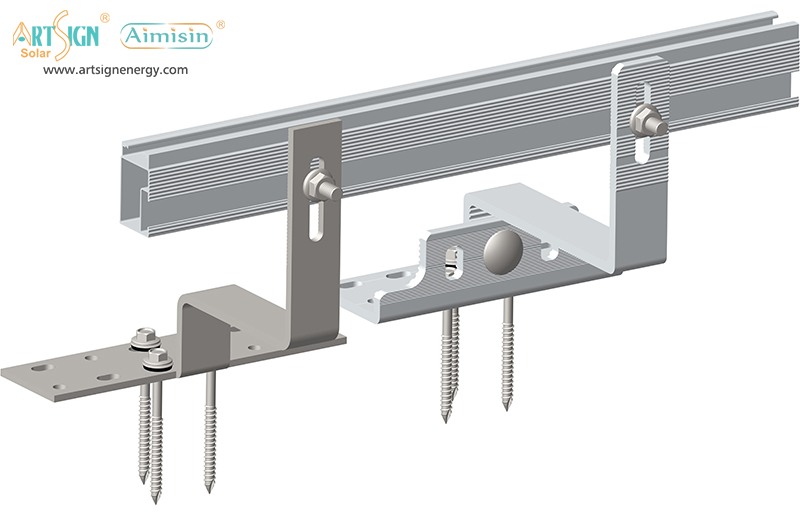
Solar panel mounting brackets connect solar panels to their installation areas, whether on rooftops, ground mounts, or poles for stability. Brackets support the solar panels by maintaining the proper angle position while they withstand wind force to secure your investment.
Good solar panel brackets improve system lifetime and boost its power generation performance. Poor hanging methods include putting solar panels in the wrong position and creating unreliable energy systems, plus expensive damage costs.
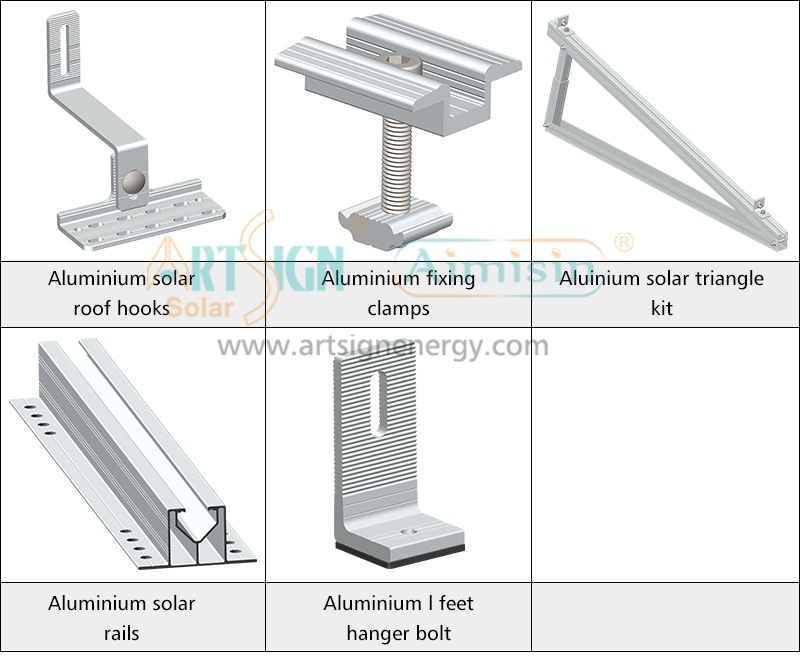
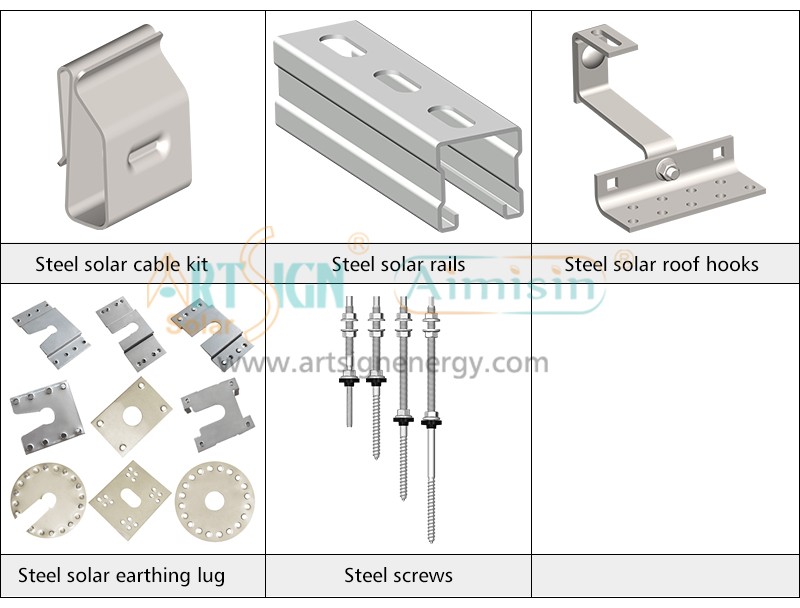
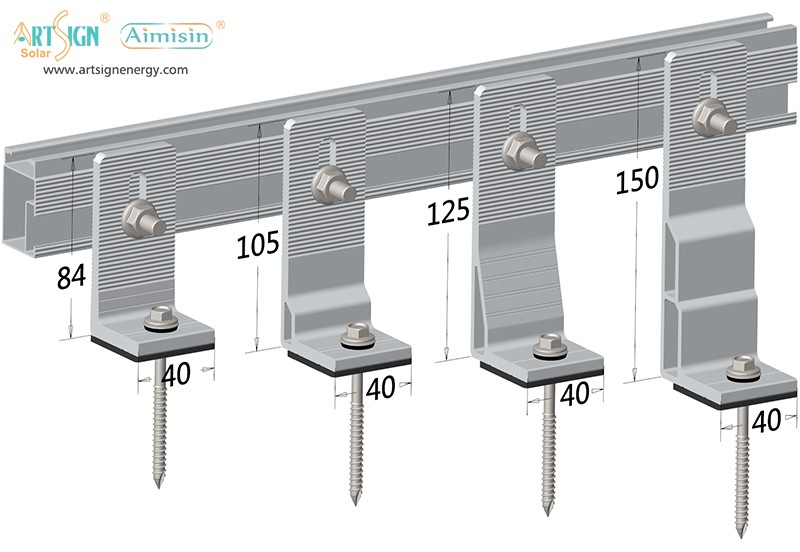
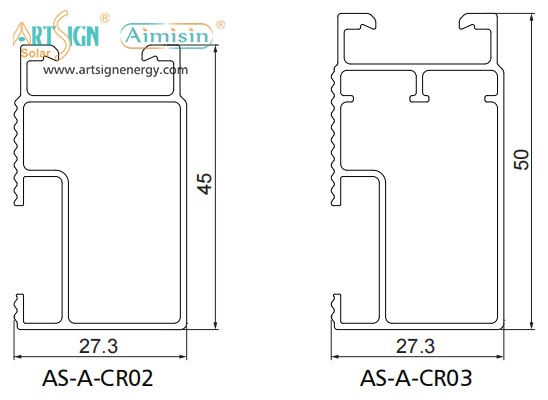
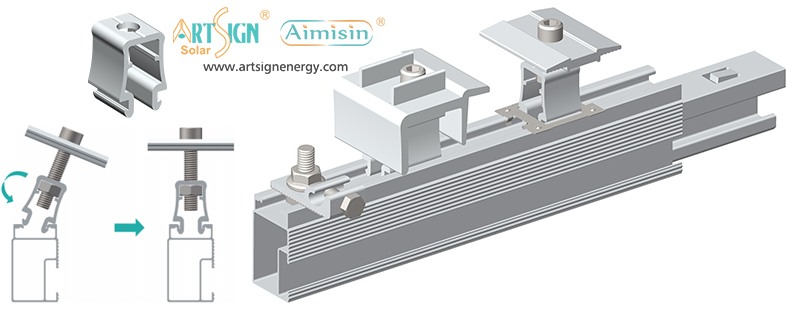
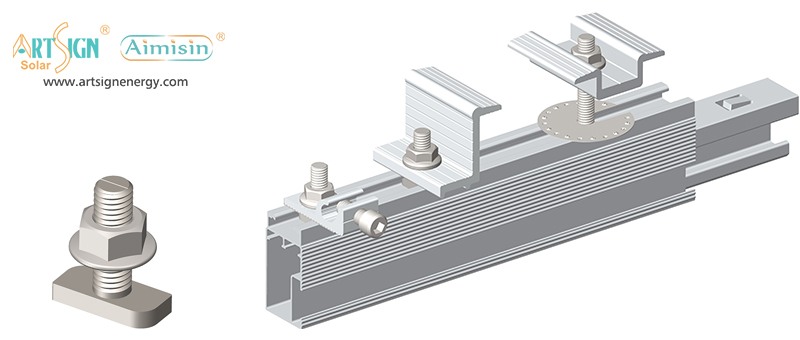
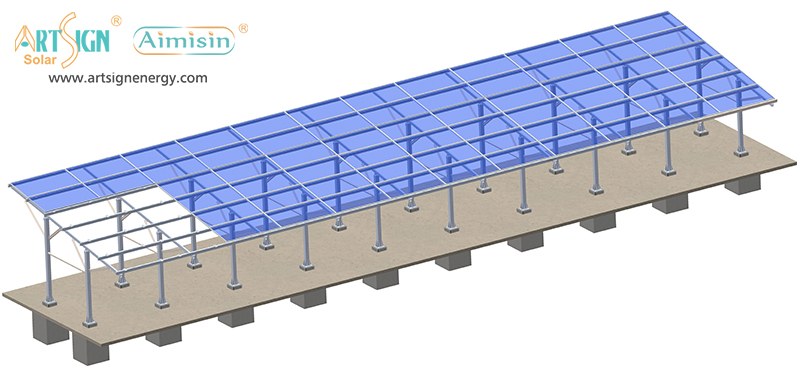
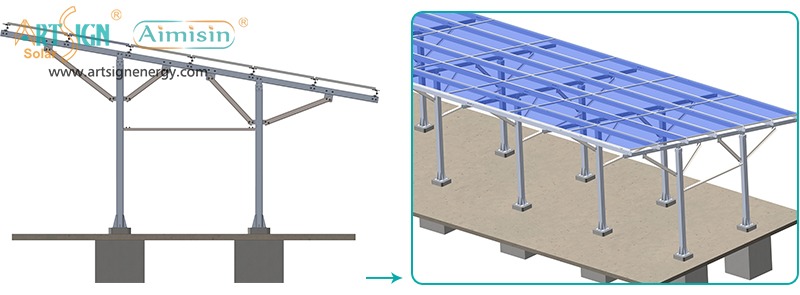
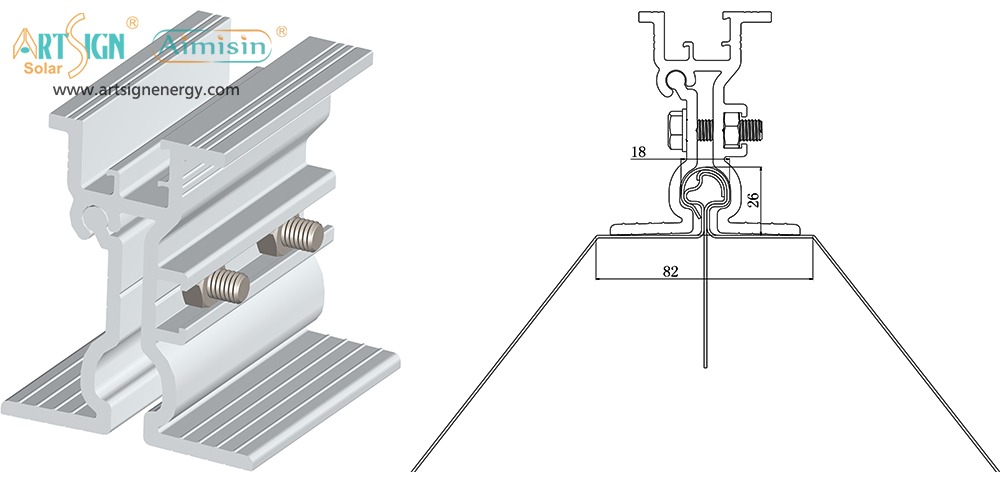
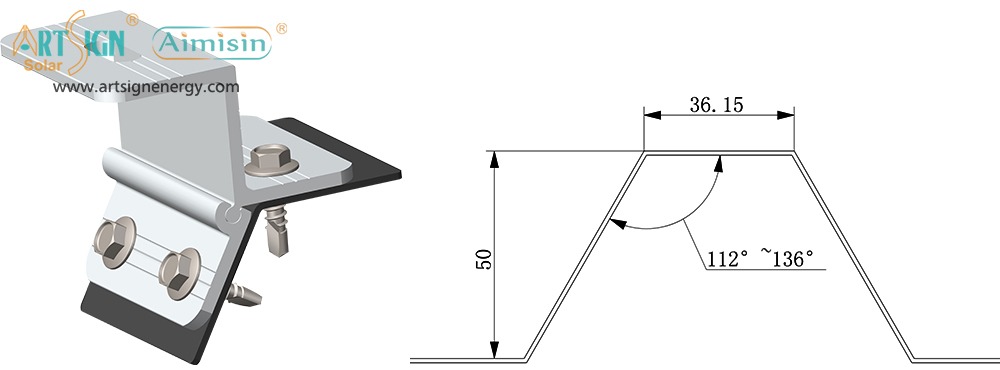
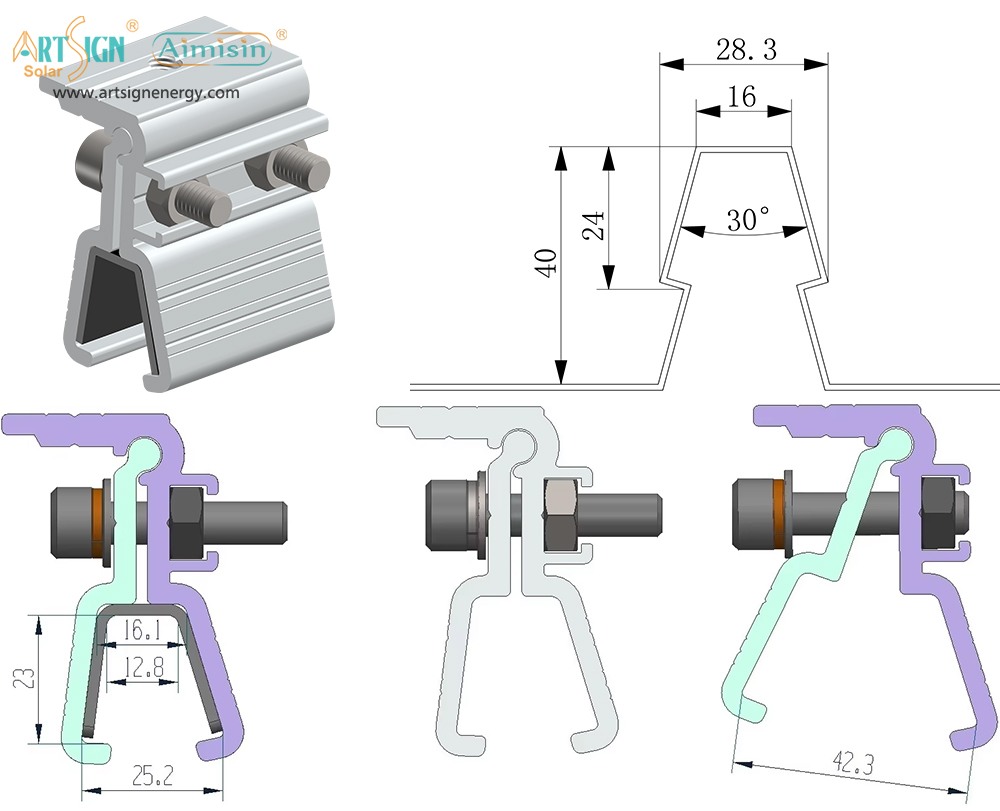
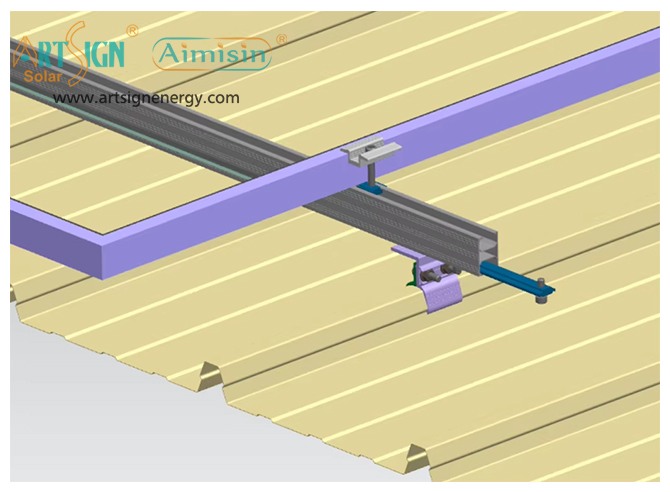
Types of Solar Panel Installation Brackets
Every building and weather environment requires its own unique solar panel bracket setup. The ideal bracket choice depends on the kind of roof you have, combined with local weather conditions and your panel angle and funding options.
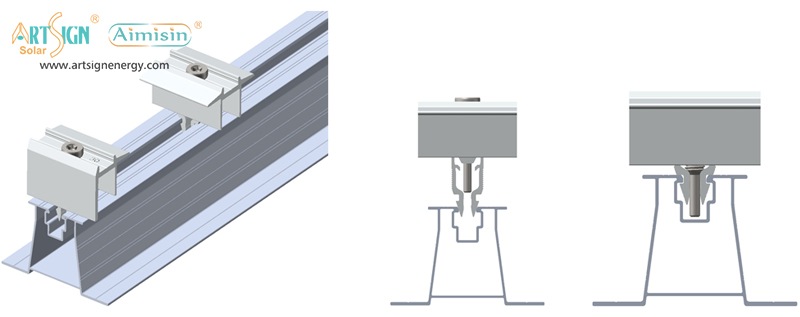
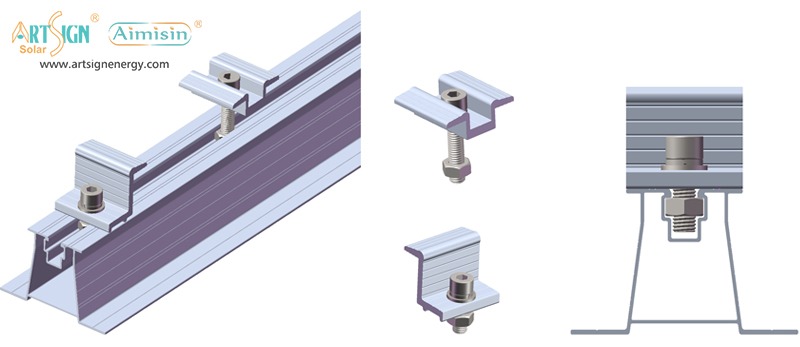
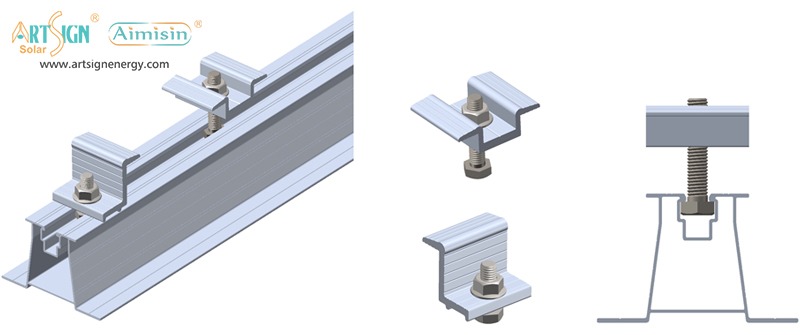
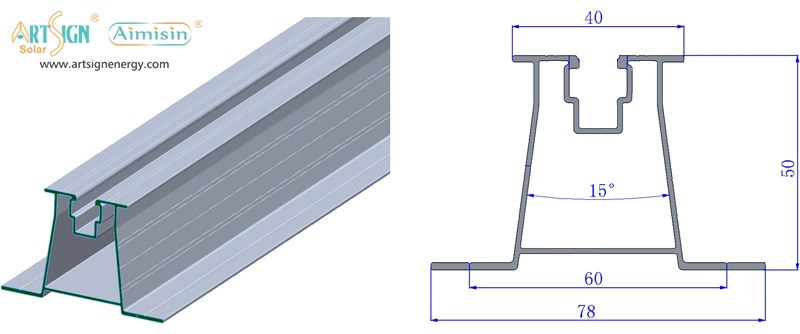
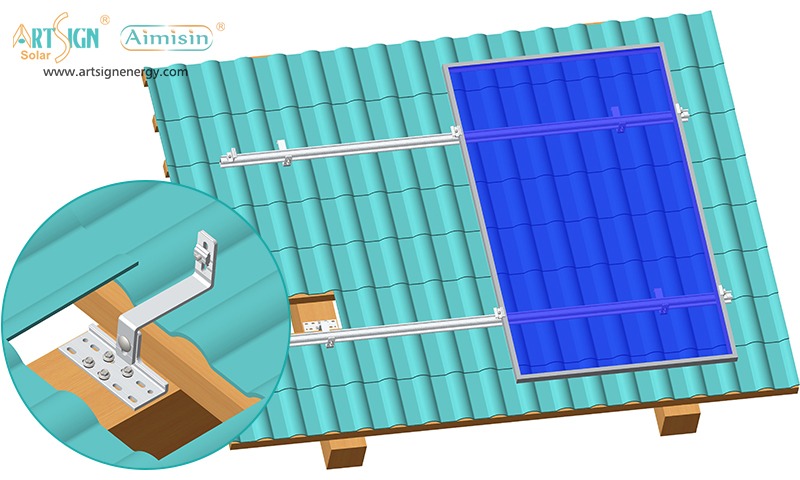
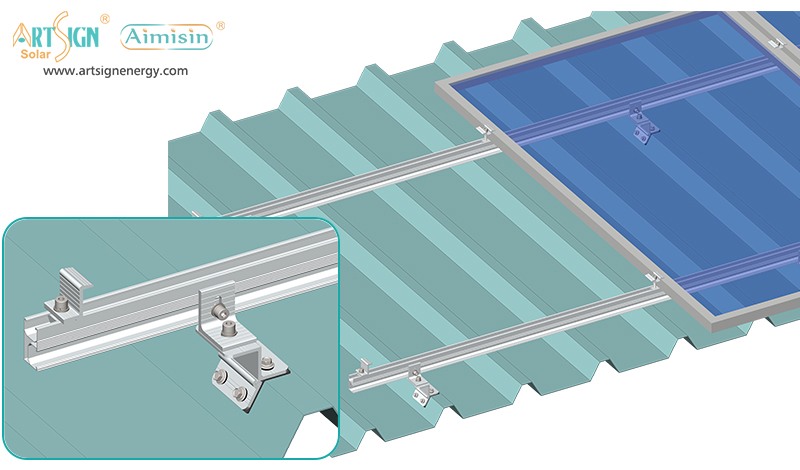
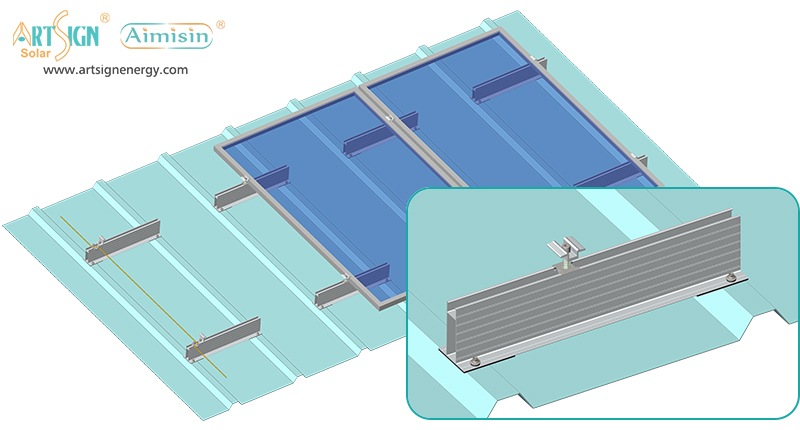
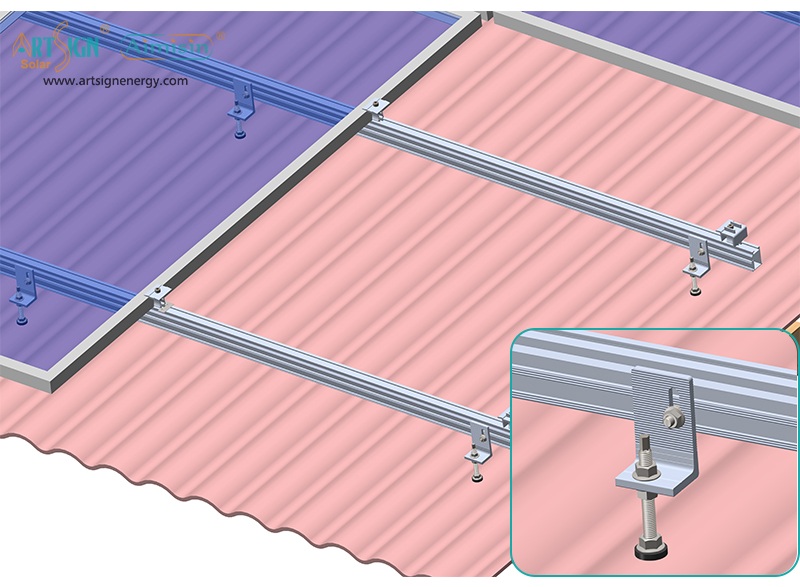
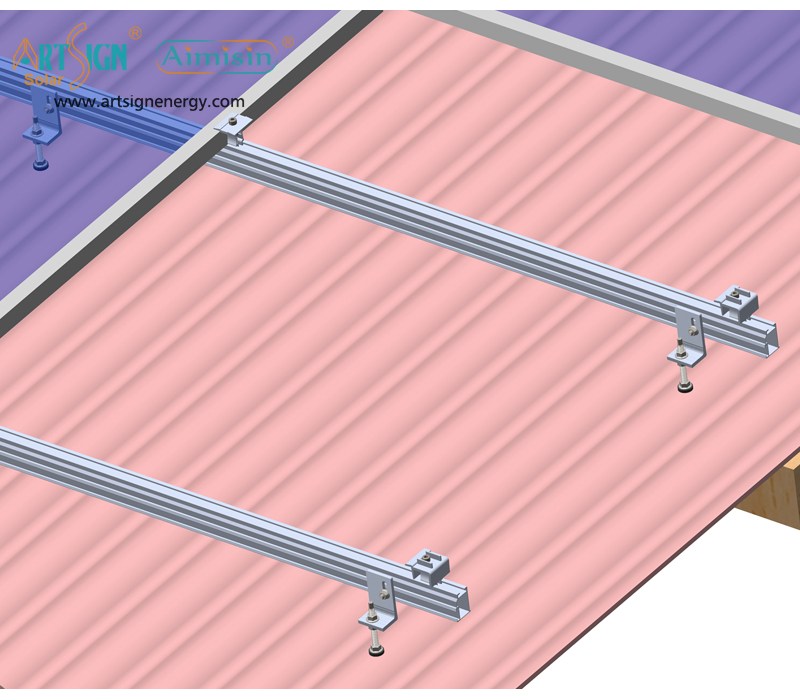
1. Roof-Mounted Brackets
These solar panel installation brackets work best for home roofs with direct mounting to the building frame. Many people choose this option because they find the system affordable and it needs only a small area of land. Common types include:
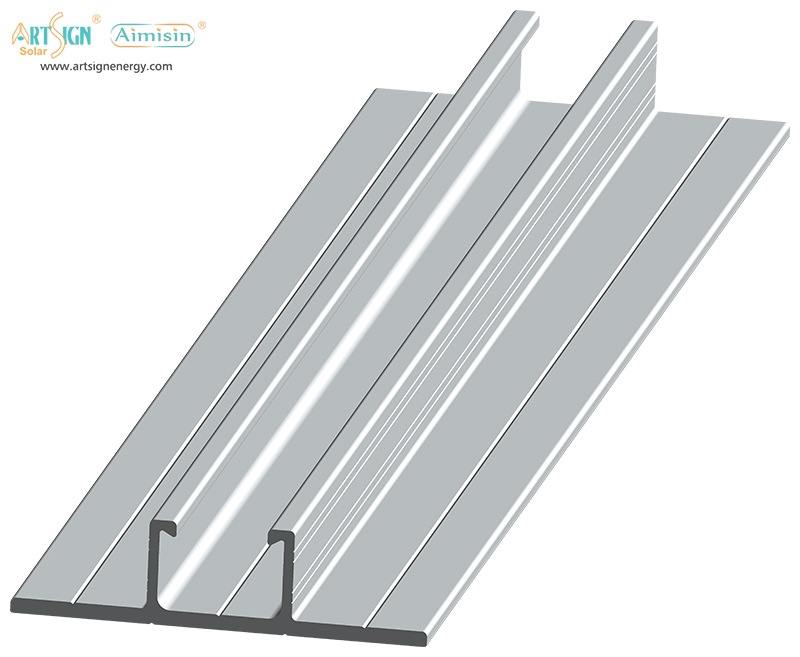
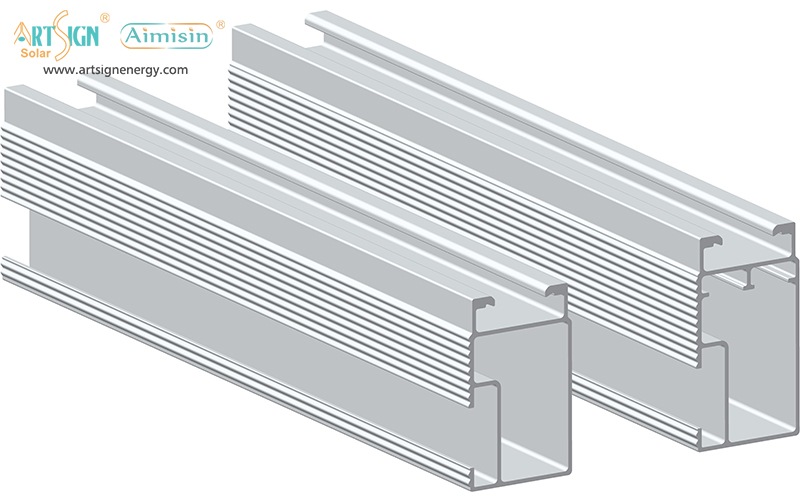
- Rail systems
- Rail-less systems
- Shared-rail systems
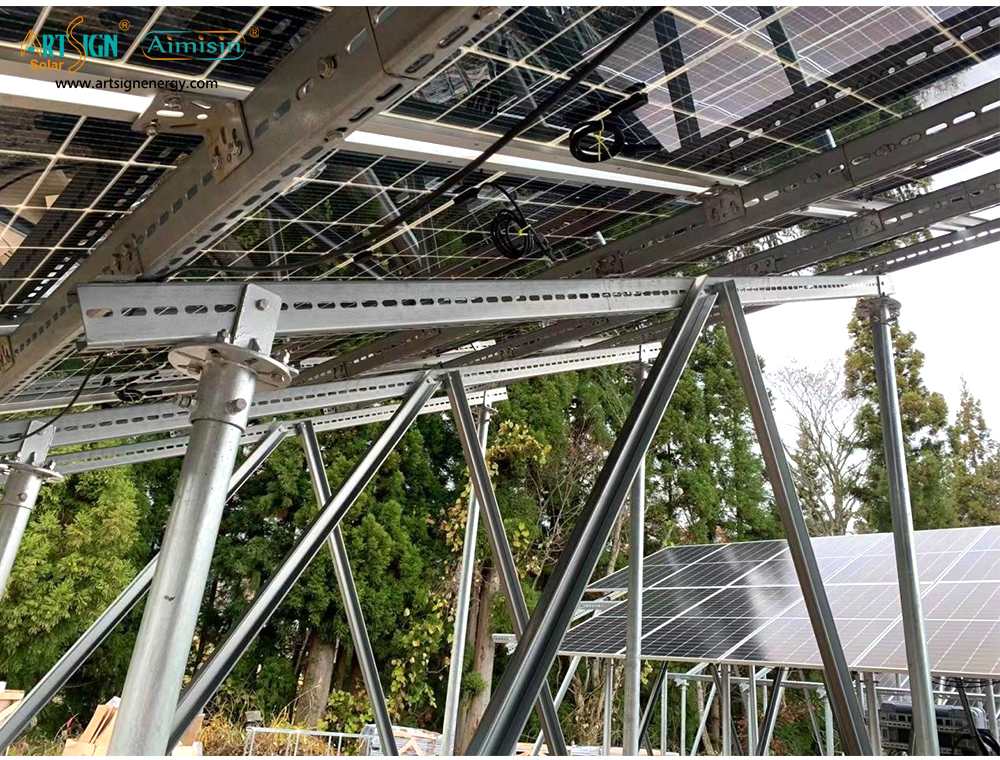
2. Ground-Mounted Brackets
Solar panels that need sunlight and space should instead be mounted on the ground. These allow for better cooling and easier maintenance.
3. Pole-Mounted Brackets
Pole mounts elevate the panels to create free air flow between them and help users position them at any angle. These structures work well in power systems that run without city power or in remote areas.
Why Mounting Brackets for Solar Panels Matter
Quality solar panels yield better results when installed appropriately.
1. Durability Against Harsh Conditions
Brackets that are made strong enough can protect panels against tough winds, snowy days and hot weather. Solar panel support systems need to be built to remain structurally strong throughout several decades of use.
2. Correct Tilt and Orientation
The panel tilt angle significantly affects the system's energy production. Solar panel brackets let you set the right angle for receiving sunlight in all seasons.
3. System Safety
Doubled solar panel brackets in improper installations create safety problems including, unhinged panels and roof leaking accidents. Top-quality brackets ensure no worries about your installation.
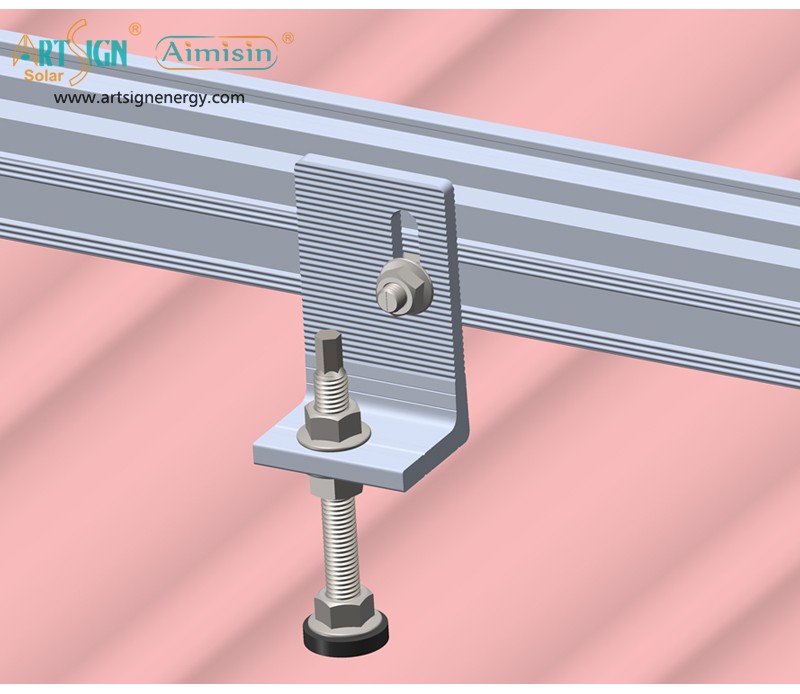
Features to Look for in Solar Panel Brackets Mountings

The buying process for solar mounting solutions easily overwhelms most customers. But here’s what really matters:
- Material Quality: Choose solar mounting systems made from aluminum or stainless steel since they resist corrosion.
- Wind/Snow Load Rating: Examine solar panel mounting accessibility before setting up your stand to match regional weather information.
- Ease of Installation: Installing solar panel brackets differs between products that require no DIY expertise and those that need professional setup.
- Compatibility: Your mounting system needs to match your panel size, layout and fixable area.
- Adjustability: Solar panel holders that change their angle let devices catch more sunlight during all season changes.
Comparing the Best Solar Panel Brackets on the Market
In your search for many different brand choices, you must carefully evaluate them. Focus on purchasing bracket systems with international test results that come with warranty protection.
During research, enter these specific search terms into your search engine.
- “Best solar panel installation brackets for tile roofs”
- “Durable mounting brackets for solar panels in coastal regions”
- “Adjustable solar panel brackets mountings for seasonal changes”
Installing Solar Panel Mounting Brackets: DIY or Professional?
People who enjoy home projects often build solar panels but choosing professional or DIY installation brings different benefits and disadvantages.
DIY Installation
The system includes all needed hardware and installation steps for someone who feels comfortable working on rooftops. Follow all required safe practices when doing this task.
Professional Installation
Professional services prevent solar panel bracket installation errors on the first try. Having experts install your brackets will protect you from problems that could arise later.
Need Help Choosing the Right Brackets?
Contact an expert or visit trusted review sites to choose solar panel brackets that meet your needs effectively. You need to install the solar panels correctly to match panel selection efforts.